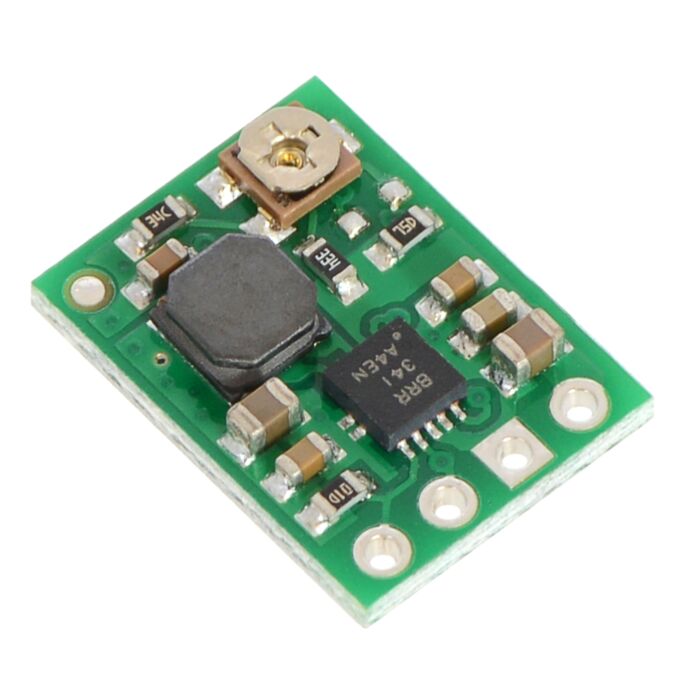
Pololu Adjustable Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V11A
In stock, ships same business day if ordered before 2PM
Fastest delivery: Tomorrow*
Disclaimer:
For next-day delivery, the shipping address must
be in the AusPost next-day network, eParcel Express must be selected, and the order must be placed
before 2PM AEST Mon-Thurs excluding NSW Public Holidays. Orders may be delayed due to AusPost
pickup timings and order verifications. eParcel Express is typically a 1-day service within the
AusPost next-day network, though it is sometimes 2+ days.
Quantity Discounts:
- 10+ $14.57 (exc GST)
- 25+ $14.12 (exc GST)
 |
This adjustable boost (step-up) voltage regulator generates higher output voltages (between 2 V and 5.25 V) from input voltages as low as 0.5 V, and it also automatically switches to a linear down-regulation mode when the input voltage exceeds the output. This makes it great for powering electronics projects from 1 to 3 NiMH, NiCd, or alkaline cells or from a single lithium-ion cell. Additionally, unlike most boost regulators, this unit offers a true shutdown option that turns off power to the load (with typical boost regulators, the input voltage will pass directly through to the output when they are disabled).
When boosting, this module acts as a switching regulator (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) and has a typical efficiency between 70% to 90%. The available output current is a function of the input voltage, output voltage, and efficiency (see Typical Efficiency and Output Current section below), but the input current can typically be as high as 1.2 A. This regulator is also available with a fixed 3.3 V or fixed 5 V output, and very similar regulators are available in a much smaller size with a fixed 3.3 V or fixed 5 V output.
The regulator’s thermal shutdown engages at around 140°C and helps prevent damage from overheating. It does not have reverse-voltage protection.
 |
Features
- Input voltage: 0.5 V to 5.5 V
- Adjustable output voltage from 2 V to 5.25 V
- True shutdown option that turns off power to the load
- Automatic linear down-regulation when the input voltage is greater than the output voltage
- 1.2 A switch allows for input currents up to 1.2 A
- Good efficiency at light load: <1 mA typical no-load quiescent current, though it can exceed 1 mA for very low input voltages (<100 µA typical quiescent current with SHDN = LOW)
- Integrated over-temperature shutoff
- Small size: 0.45" × 0.6"; × 0.1" (11.5 × 15.3 × 2.5 mm)
Using the Regulator
Connections
The boost regulator has four connections: shutdown (SHDN), input voltage (VIN), ground (GND), and output voltage (VOUT).
The SHDN can be driven low (typically under 0.4 V) to power down the regulator and turn off power to the load (unlike most boost regulators, the input power does not pass through to the output when the board is disabled). This pin is internally pulled up to VIN through an 100 kO resistor, so it can be left disconnected or connected directly to VIN if you do not need to use the disable feature. The disable threshold is a function of the input voltage as follows:
- For VIN < 0.8 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.1×VIN to disable the regulator and above 0.9×VIN to enable it.
- For 0.8 V = VIN = 1.5 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.2×VIN to disable the regulator and above 0.8×VIN to enable it.
- For VIN > 1.5 V, SHDN voltage must be below 0.4 V to disable the regulator and above 1.2 V to enable it.
The input voltage, VIN, must be at least 0.5 V for the regulator to turn on. However, once the regulator is on, the input voltage can drop as low as 0.3 V and the set output voltage will be maintained on VOUT. Unlike standard boost regulators, this regulator has an additional linear down-regulation mode that allows it to convert input voltages as high as 5.5 V down to lower output voltages for small to moderate sized loads (for example, in Pololu's tests, this regulator was able to supply 300 mA while converting an input of 5.5 V down to 1.8 V). When the input voltage exceeds the output voltage, the regulator automatically switches to this down-regulation mode. The input voltage should not exceed 5.5 V. Please be wary of destructive LC spikes that might cause the input voltage to surpass 5.5 V (see below for more information).
The four connections are labeled on the back side of the PCB, and they are arranged with a 0.1" spacing along the edge of the board for compatibility with solderless breadboards, connectors, and other prototyping arrangements that use a 0.1" grid. You can solder wires directly to the board or solder in either the 4×1 straight male header strip or the 4×1 right-angle male header strip that is included.
 |
Setting the Output Voltage
The output voltage can be adjusted using a multimeter and a light load (e.g. a 1 kO resistor). Turning the potentiometer clockwise increases the output voltage. The output voltage can be affected by a screwdriver touching the potentiometer, so the output measurement should be done with nothing touching the potentiometer (also, note that touching parts of the board with your finger can affect the output voltage). The following graph shows the approximate output voltage as a function of the potentiometer position:
 |
Output voltage settings for Pololu adjustable step-up voltage regulator U1V11A. |
|---|
Please note that the output voltage can be set below 2 V at the low end of the potentiometer’s range and above 5.25 V at the high end. While this should not harm the regulator, it might not work reliably or its output could become unstable when the output voltage is not within the recommended 2 V to 5.25 V range. In addition, the potentiometer has no physical end stops, which means that the wiper can be turned 360 degrees and into an invalid region in which the output voltage is unstable.
Typical Efficiency and Output Current
The efficiency of a voltage regulator, defined as (Power out)/(Power in), is an important measure of its performance, especially when battery life or heat are concerns. As shown in the graphs below, this switching regulator typically has an efficiency of 70 to 90%.
The maximum achievable output current is approximately proportional to the ratio of the input voltage to the output voltage. If the input current exceeds the switch current limit (typically somewhere between 1.2 and 1.5 A), the output voltage will begin to drop. Additionally, the maximum output current can depend on other factors, including the ambient temperature, air flow, and heat sinking.
LC Voltage Spikes
When connecting voltage to electronic circuits, the initial rush of current can cause damaging voltage spikes that are much higher than the input voltage. In Pololu's tests with typical power leads (~30" test clips), input voltages above 4.5 V caused voltage spikes that could potentially damage the regulator. You can suppress such spikes by soldering a 33 µF or larger electrolytic capacitor close to the regulator between VIN and GND.
More information about LC spikes can be found in Pololu's application note, Understanding Destructive LC Voltage Spikes.
People often buy this product together with:
 | Pololu Adjustable Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S7V8A |
 | Pololu 3.3V Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V11F3 |
 | Pololu 5V Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V11F5 |
Dimensions
| Size: | 0.45" × 0.6" × 0.1"1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 0.7 g1 |
General specifications
| Minimum operating voltage: | 0.5 V |
|---|---|
| Maximum operating voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Maximum input current: | 1.2 A2 |
| Minimum output voltage: | 2 V |
| Maximum output voltage: | 5.25 V |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | N |
| Maximum quiescent current: | 4 mA3 |
Identifying markings
| PCB dev codes: | reg12a |
|---|---|
| Other PCB markings: | 0J7440 |
Notes:
- 1
- Without included optional headers.
- 2
- Regulator may overheat at lower input currents when VIN is much lower than VOUT. Available output current is a function of VIN, VOUT, and the regulator efficiency.
- 3
- The highest quiescent currents occur at very low input voltages; for most of the input voltage range, the quiescent current is well below 1 mA.
File downloads
-
Pololu Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V11x schematic diagram (177k pdf)
Printable schematic diagram for the U1V11x family of Pololu step-up voltage regulators: U1V11A, U1V11F3, and U1V11F5.
-
Dimension diagram of the U1V11x family of step-up voltage regulators (229k pdf)
-
Drill guide for step-up voltage regulator U1V11x (21k dxf)
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes.
Recommended links
Exact shipping can be calculated on the view cart page (no login required).
Products that weigh more than 0.5 KG may cost more than what's shown (for example, test equipment, machines, >500mL liquids, etc).
We deliver Australia-wide with these options (depends on the final destination - you can get a quote on the view cart page):
- $3+ for Stamped Mail (typically 10+ business days, not tracked, only available on selected small items)
- $7+ for Standard Post (typically 6+ business days, tracked)
- $11+ for Express Post (typically 2+ business days, tracked)
- Pickup - Free! Only available to customers who live in the Newcastle region (must order online and only pickup after we email to notify you the order is ready). Orders placed after 2PM may not be ready until the following business day.
Non-metro addresses in WA, NT, SA & TAS can take 2+ days in addition to the above information.
Some batteries (such as LiPo) can't be shipped by Air. During checkout, Express Post and International Methods will not be an option if you have that type of battery in your shopping cart.
International Orders - the following rates are for New Zealand and will vary for other countries:
- $12+ for Pack and Track (3+ days, tracked)
- $16+ for Express International (2-5 days, tracked)
If you order lots of gear, the postage amount will increase based on the weight of your order.
Our physical address (here's a PDF which includes other key business details):
40 Aruma Place
Cardiff
NSW, 2285
Australia
Take a look at our customer service page if you have other questions such as "do we do purchase orders" (yes!) or "are prices GST inclusive" (yes they are!). We're here to help - get in touch with us to talk shop.
Have a product question? We're here to help!
Videos
View AllGuides
PiicoDev Magnetometer- Getting Started Guide
The Maker Revolution
How to Use DC Regulators/Converters
Powering Portable Projects: Batteries
Projects
Wireless QI Phone Charger Powered by Raspberry Pi
mmPi-Pico HAT
Solar Charging Station
Makers love reviews as much as you do, please follow this link to review the products you have purchased.




















Product Comments